

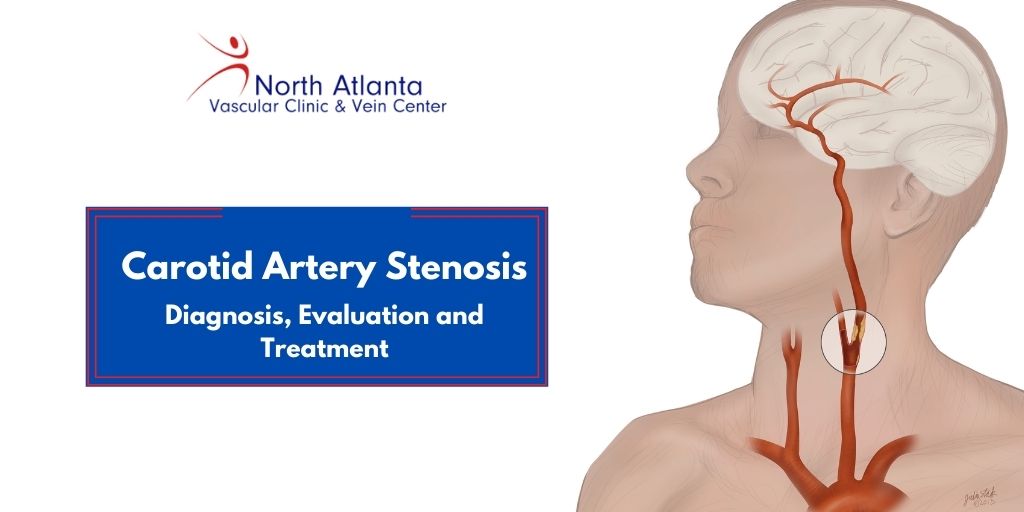

Carotid artery stenosis is the narrowing of carotid arteries on both sides of the neck that carry blood to the brain, face, and head. A condition called atherosclerosis builds up plaque within the arteries and decreases the blood flow, which causes carotid artery stenosis. If ignored, stenosis can lead to a stroke because it completely narrows the arteries that carry blood to the brain.
These factors increase the risk of developing carotid artery stenosis:
Some people with this condition may experience blurred vision, fainting, and dizziness, which indicate insufficient blood supply to the brain. Generally, the first sign of carotid artery stenosis is a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) due to a blood clot in the blood vessel affected by atherosclerosis. When this clot gets dislodged, it can travel to the brain and plug up a smaller artery. This can be life-threatening. It can damage the section of the brain that is dependent on the blood vessel.
Symptoms of both a stroke and a TIA include:
Sudden numbness or paralysis (often on one side of the body)
TIA is a temporary occlusion of a small artery that lasts a few minutes without causing any lasting damage. However, it is considered a warning sign of carotid artery stenosis. A stroke causes permanent injury to the part of the brain due to a lack of blood supply, resulting in severe disability or death.
Your doctor will analyze your medical history and conduct a physical examination. The physical exam often includes listening for an abnormal sound in the damaged artery. Your doctor may then assess your mental and physical capacities, including memory, strength, and speech.
Doctors generally perform these tests to diagnose your condition:
Your doctor may recommend any of the following treatments depending on your health and severity of the condition.
Contact or schedule an appointment with our vascular health experts at North Atlanta Vascular Clinic and Vein Center today if you need the treatment for carotid stenosis in Johns Creek. You can also get in touch with us for any questions about vascular disease.